Preface:
This main question “website speed test is important?” and “website speed optimization is not important?” .the speed test and website optimization are twins and And they mean it together. without any speed test, we are not able to tune-up our speed optimization. In a glance review the following statistic about the one-second delay in page load time yields and after that think seriously about your speed optimization:
- 1% fewer page views
- 16% decrease in customer satisfaction
- 7% loss in conversions
This means that having a fast site is essential and not just for ranking well with Google, but for keeping your bottom-line profits high.
In fact, 47% of consumers expect websites to load in two seconds or less and 40% will abandon a page that takes three or more seconds.
This means that if your site takes more than three seconds to load, so you lose almost half of your visitors before they even arrive on your site.so seriously thinking about website speed optimization. In this article, we want to explain how you can do your website speed optimization.
What are Website speed test and website speed optimization?
The page speed essentially refers to the length of time-cycle at which web pages or other content is downloaded from website hosting servers and should be displayed onto the requesting web browser. Page load time is the duration between clicking the link and displaying the entire content from the web page on the requesting browser.
Although the term website speed optimization is not the pure scientific term in short definition; Website optimization encompasses all the technical and marketing techniques used to obtain traffic, so engage visitors and then convert them into prospects or customers using a clearly defined method that meets a number of pre-defined goals.
Site speed is one of the most critical performance indicators of all:
It’s estimated that you risk losing traffic when a site takes over 2.5-3 seconds to load and that the abandon rate shoots up after 5 seconds.
A site can be slowed down for a number of reasons. However, there are several (fantastic) tools that will give you a quick appraisal of the situation:
By boosting speed, you cut abandons caused by slow loading and also help to improve your SEO.
Performance plays a major role in the success of any online venture. Here are some case studies that show how high-performing sites engage and retain users better than low-performing ones:
- Pinterest increased search engine traffic and sign-ups by 15%when they reduced perceived wait times by 40%.
- COOK increased conversions by 7%, decreased bounce rates by 7%, and increased pages per session by 10%when they reduced average page load time by 850 milliseconds.
Here are a couple of case studies where low performance had a negative impact on business goals:
- The BBC found they lost an additional 10% of users for every additional second their site took to load.
- DoubleClick by Google found 53% of mobile site visits were abandoned if a page took longer than 3 seconds to load.
In the same DoubleClick by Google study cited above, it was found that sites loading within 5 seconds had 70% longer sessions, 35% lower bounce rates, and 25% higher ad viewability than sites taking nearly four times longer at 19 seconds. To get a rough idea of how your site’s performance compares with your competitors, check out the Speed Scorecard tool.
Totally website speed is the average of a sample of load times of a few pages on your site, and therefore not a very in-depth way of determining your site’s true performance.
How a web page loaded?
What are the steps of a webpage being displayed? The following steps are shown us the hierarchy of page loading steps:
- A request is made when a link is clicked.
- page and its resources (files) are downloaded.
- web browser uses the page resources to build the page.
- The page then is rendered (displayed) to the user.

Each of the above steps has many components and details, but those four steps are the main things that happen to display a webpage to a user.

This article will discuss each of these steps to provide an overview of what actually happens when a webpage is displayed in a browser.
Technically the four steps listed above are often referred to more technically as…
- Request
- Response
- Build
- Render
Each of these steps is often performed several times during a page load.SO Page load time is the time it takes to download and display the entire content of a web page in the browser window (measured in seconds).
How page load time works:
The “stopwatch” begins when a user makes a request and ends when the entire content of the page is displayed on the requesting browser. Below is a typical request-response cycle with various steps that contribute to page load time:
- A user enters a URL, submits a form, or clicks on a hyperlink
- The browser makes a request to the server through the network
- Each request is processed by the webserver
- A web server sends the response back to the browser
- The browser starts receiving the requested page (known as the time to first byte)
- The browser parses, loads, and renders the page content
- Entire requested page becomes available on the browser

How to improve page load time
There are many ways to improve this metric, but here are some of the most common. In the following shortlist you can find the main headlines of improving pages load time:
- File Compression: Reduces the size of the CSS, HTML, JavaScript, images, and other web elements. (Check out ImageOptim for Mac to compress images).
- Minification: Optimizes the code by removing unused code, white spaces, comments, etc.
- Reducing redirects: Each time a web page redirects the browser to another server, the user faces an additional time for the request-response cycle to complete. Best to get rid of these if possible.
- CDN: A content delivery network (CDN) puts content geographically closer to your users so they can receive it quicker.

What is the benefit of website speed optimization? (Use the website speed test)
A 2010 study by Gomez, titled “Why Web Performance Matters: Is Your Site Driving Customers Away?”, that interviewed 1,500 consumers about how website performance impacts their shopping experience, revealed the following insights:
An increase in website loading time from 2 to 10 seconds increased page abandonment rate by 38%. During peak traffic periods, more than 75% of consumers left for a competitor’s website instead of suffering a delay.
Many other studies have been published on the impact of website speed, and all of them approximately mentioned that a one-second delay in site loading time resulted in a 7% decrease in conversions, an 11% decrease in page views and a 16% decrease in customer satisfaction. It’s also important to note that Google now uses website speed as a ranking factor.
Totally, having a slow website will negatively impact the following:
- Traffic and page views
- Conversions
- Sales
- Brand image and perception in the mind of your visitors

There are many benefits to individually optimizing each page’s speed, although one of the most obvious is for better user experience.
Improve User Experience
The main reason to speed up a website is to improve the visitor’s experience. Even without Google’s concerns about speed, many users will abandon a website with poor performance. Most website owners make a great effort to engage visitors through their content and graphics, but the real first impression is their website loading time. Since 1994, research has demonstrated how in terms of usability speed is a major need. Users need a fast response in order to freely navigate and explore the content and their attention would collapse at loading times beyond the 10 seconds.
Google has reported that a 1-second delay in load time will decrease visitors’ satisfaction by 16% and 79% of those visitors would not buy if they are not satisfied with website performance.
E-commerce owners also lost the confidence of visitors when having slow and bloated websites. Slow websites are related to a lack of efficiency and fail to gain a visitor’s trust to share personal and billing information. In addition, customers would remember loading times as being 35% longer than they actually are. So, having speed as a priority and reducing website loading times as much as possible, will have an enormous effect on their revenues and general conversion.
Achieve marketing goals
Optimizing your site to accelerate the loading time will help you to reach your marketing goals and SEM. No matter if you are looking to improve conversion, reduce bounce rate, sales or just improving the service for your customers. There is a lot of evidence showing the effect of a fast website on all these metrics, especially for the effect on revenues.

Conversion and Revenues
Going back to visitor’s experience and confidence, some studies have shown that in England 67% online shoppers will abandon a purchase on a slow website and also that Improving 1 second a website loading time will increase the conversion rate between 10% and 20%. In addition, the Online Retail Performance Report made by Akamai in 2017 shows how 50% of consumers browse for products and services on their smartphones and also that a 100-millisecond delay could hurt conversions by 7%. So, e-commerce success is highly dependent on delivering a good experience, especially on mobile devices.
Another study made by the Aberdeen Group shows how a 1-second delay leads to a 7% loss in conversions. That means, that if your website earns around $10.000 each day, you will loss $250.000 each year. In general, terms, since 1997 was demonstrated that optimal conversion is reached at 2 seconds
Traffic
Web owner’s first digital strategy is to attract visitors to their websites. No matter if they pay or position their pages organically; website loading time would also affect the number of views. Google studies have shown that a delay of just half a second caused a 20% loss in traffic, and a second delay turns on 11% fewer page views.
Facebook Reach
It is important for Facebook to display stories that link to fast websites. So, since 2017 it displays such websites first on the newsfeed. Stories that are slow to load cause frustration on Facebook users, so, they will locate them on the bottom of the reading list. Speeding up your website will then improve your Facebook Reach and engagement.
SEO Positioning
In order to be found in the universe of the internet, websites have to accomplish good scores according to the Google PageRank algorithm. Website loading time is included, but also some user experience metrics such as bounce rate and page views. Google’s main goal is to satisfy visitor’s needs, so it penalizes with a lower rank the sites that fail to offer value to their visitors.
For example, a website loading in 10 seconds increases the bounce rate probability by 123%. By the other side optimizing a website to load in 2 seconds reduces the bounce rate from 32.3% to 9.61%. Under the same loading time (2 seconds), users visit an average of 5,6 pages more; which means a higher likelihood of adding items to the cart for e-commerce sites. Finally, increased website speed means an increase in the number of pages Google can crawl and index. The more pages that are indexed, the higher the chance that you will have that individual page rank
How to make website speed optimization? (for best results in website speed test)
There are tons of factors that influence how long each page on your site takes to load, so there are many different steps you can take to increase your speed and improve user experience. While all of these tips can help you improve your site speed, you don’t need to do all of them today.
If you’ve tuned up on your site speed in the past, currently your site may already be in line with some of these best practices. In this post, we’ll go over 14 tips and best practices you can use to decrease your load times and improve your site’s performance.
1. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A content delivery network is a set of web servers distributed across various geographical locations that provide web content to end-users with regard to their location. When you host the website on a single server, all user’s requests are sent to the same hardware. For this reason, the time needed to process each request increases. On top of that, the load time increases when users are physically far from the server. With CDN, user requests are redirected to the nearest server. As a result, the content is delivered to a user quicker and a website works faster. This is a rather expensive, but quite effective way to optimize the load time.

2. Move your website to a better host
There are three possible types of hosting:
- Shared hosting
- Virtual Private Servers (VPS) hosting
- Dedicated server
The most popular type of hosting that is used all over the world is sharing hosting. That’s the cheapest way to get your site online in a short time and for a low fee. It’s essential to choose the fast web host to ensure better optimization. With shared hosting, you share CPU, disk space, and RAM with other sites that also use this server. This is the main reason why shared hosting isn’t as fast as VPS or a dedicated server.

Virtual Private Servers and dedicated servers are much faster. VPS uses multiple servers for content distribution. Having VPS you share the server with its other users and have your own part of the virtual server where your configurations don’t influence other clients. If your website has the average traffic or you have the e-commerce site with traffic spikes in some periods, VPS will be the optimal solution for you.
The most expensive hosting option is to use a dedicated server which can be your own physical server. In this case, you pay a server rent and hire a system administrator to maintain it.
Another approach is to rent dedicated cloud resources from AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google, or other public cloud providers. Both approaches can also be combined into a hybrid cloud that we discussed recently. With dedicated servers, all resources belong only to you and you get full control of it. Cloud infrastructures can also add unlimited and on-demand scalability under a number of packages.
Serverless architecture is yet another option that removes maintenance and server set up procedures altogether. Consider reading our separate article covering serverless architecture specifics and benefits.
3. Optimize the size of images on your website
Everyone loves eye-catching images. In the case of successful eCommerce sites, images are the vital part. A lot of photos, images, graphics on your product pages improve engagement. the negative side of the image use is that they are usually large files that slow down a website.
The best way to reduce the image size without compromising its quality is to compress images using such tools as ImageOptim, JPEGmini, or Kraken. The procedure may take a bit of time but it’s worth it. Another way to reduce the image size is to use the HTML responsive images <secret> and <size> attributes that adjust image size based on user display properties.
4. Reduce the number of plugins
Plugins are common components of each website. They add specific features suggested by third parties. Unfortunately, the more plugins are installed, the more resources are needed to run them. As a result, the website works slower and also security issues can appear. As time passes, the number of plugins grows, while some of them may not be used anymore. We recommend checking out all the plugins you have installed and deleting unnecessary ones. First, run the performance tests on your page to find out which plugins are slowing down your website. Not only does the website speed depend on the number of installed plugins but also on their quality. Try to avoid plugins that load a lot of scripts and styles or generate a lot of database queries. The best solution is to keep only the necessary ones and ensure that they are kept up to date.

5. Minimize the number of JavaScript and CSS files
If your website contains a lot of JavaScript and CSS files, it leads to a large number of HTTP requests when your website visitors want to access particular files. These requests are treated individually by the visitor’s browsers and slow down the website’s work. If you reduce the number of JavaScript and CSS files this will undoubtedly speed up your website. Try to group all JavaScript into one and also do so with all CSS files. This will reduce the overall number of HTTP requests. There are a lot of tools to minify HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files quickly. For instance, you can use WillPeavy, Script Minifier, or Grunt tools.
6. Use website caching
In case there are a lot of users accessing the page at one-time servers work slowly and need more time to deliver the web page to each user. Caching is the process of storing the current version of your website on the hosting and presenting this version until your website is updated. This means that the web page doesn’t render over and over again for each user. The cached web page doesn’t need to send database requests each time.
The approaches to website caching depend on the platform your website is developed on. For WordPress for instance, you can use the following plugins: W3 Total Cache or W3 Super Cache. If you use VPS or a dedicated server, you can also set up caching under your general settings. In the case of the shared server, the website caching isn’t usually available.
7. Implement Gzip Compression
Gzip Compression is an effective way to reduce the size of files. It minimizes the HTTP requests and reduces the server response time. Gzip compresses the files before sending them to the browser. On the user side, a browser unzips the files and presents the contents. This method can work with all files on your website. You can enable Gzip on your website by adding some lines of the code or via a utility called gzip.

8. Database optimization in CMS
Database optimization is an effective way to increase performance. If you use a content management system (CMS) packed with complex plugins, the database size increases and your website works slower. For instance, the WordPress CMS stores comments, blog posts, and other information that take up a lot of data storage. Each CMS requires its own optimization measures and also has a number of specific plugins. For WordPress, for example, you may consider WP-Optimize.
9. Reduce the use of web fonts
Web fonts have become very popular in website design. Unfortunately, the use of web fonts has a negative impact on the speed of page rendering. Web fonts add extra HTTP requests to external resources. The following measures will help you reduce the size of web font traffic:
- Use modern formats WOFF2 for modern browsers;
- Include only those character sets that are used on the site;
- Choose only the needed styles
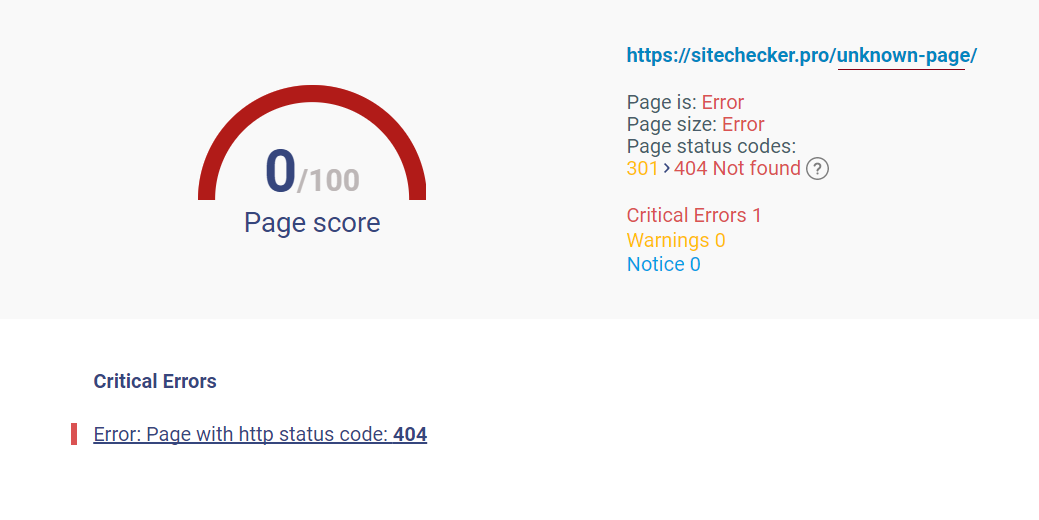
10. Detect 404 errors
A 404 error means that a “Page isn’t found”. This message is provided by the hosting to browsers or search engines when the accessed content of a page no longer exists. In order to detect and correct a 404 error, you can use error detection tools and plugins. As we mentioned, additional plugins can negatively affect your website speed, so we advise running the resource through external tools for error detection. For instance, Xenu’s Link Sleuth, Google Webmaster Tools (GWT), and 404 Redirected Plugin for WordPress.
Once you’ve detected all 404 errors, you need to assess the traffic that they generate. If these dead links no longer bring any visits and thus never consume your server resource, then you may leave them as they are. If these pages still have some traffic coming, consider setting redirects for external links and fixing the link addresses for the internal ones.
11. Reduce redirects
Website redirects create additional HTTP requests which negatively impact performance. We advise to keep them to a minimum or eliminate them entirely. First, you should identify all redirects on your page by running a site scan. You can use Screaming Frog to quickly identify redirects. Then you must check if they serve a necessary purpose and leave only the critical ones.

12. Monitor mobile page speed
In addition to monitoring your load times on desktop, you’ll want to pay particular attention to how well your site loads on mobile devices.
As we mentioned above, mobile user experience now impacts all of your site’s rankings.
Plus, it’s in your best interest to provide a fast, user-friendly site to mobile users.
You can start by using Google’s Test My Site tool to audit your own page speed. To get started, just enter your URL.

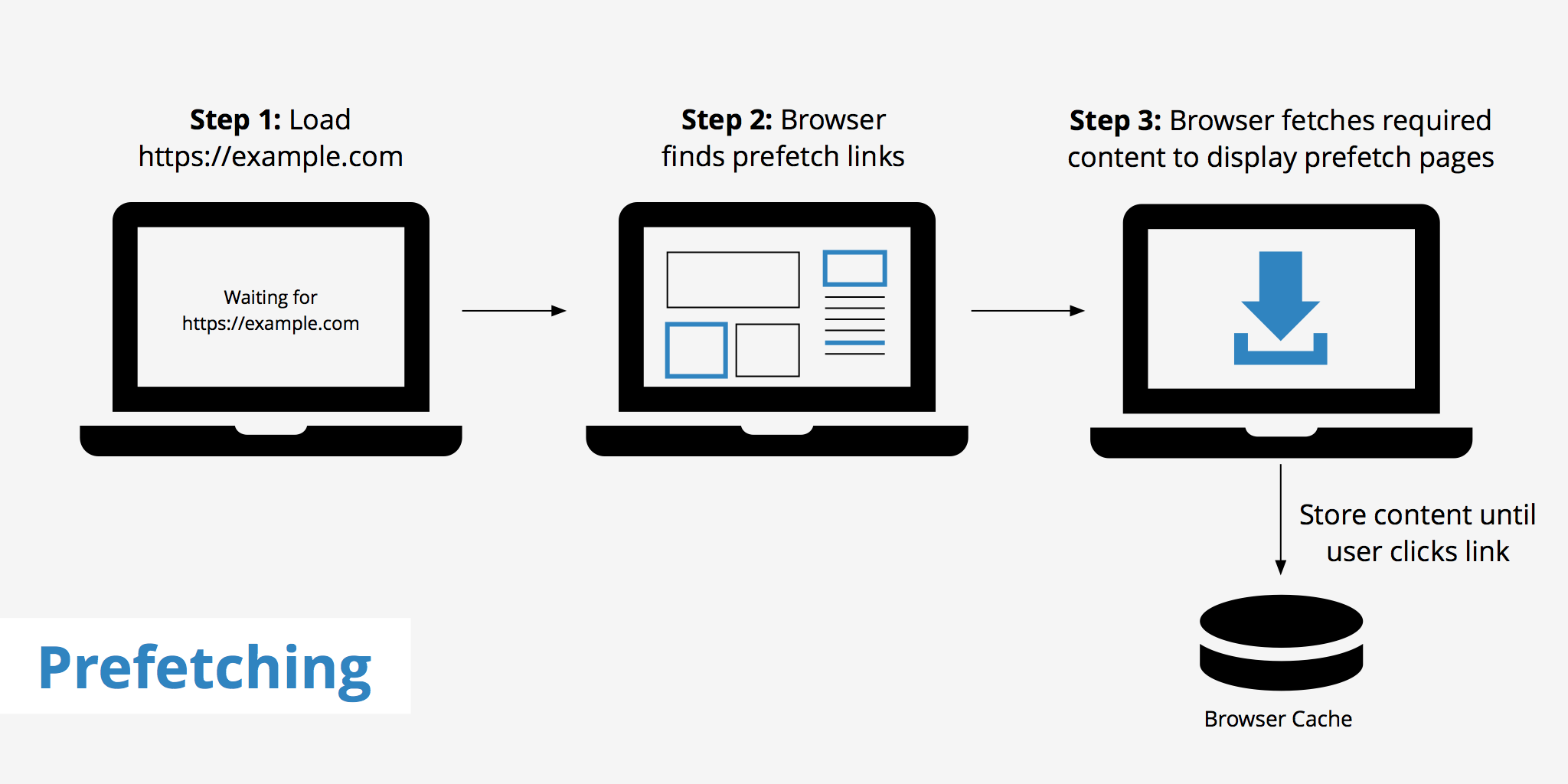
13. Use prefetching techniques
Prefetching entails reading and executing instructions before a user initiates them. The technique is rather common. It works well if you can anticipate user actions and, for instance, load some content or links in advance. Usually, modern browsers allow for prefetching by default as they assume user behavior patterns. However, UX specialists and engineers are more likely to understand user behavior and make “hints” for browsers to do prefetching work.
There are three main types of prefetching:
DNS-prefetching. The practice entails resolving domains into IP addresses in advance.
Link Prefetching. If you are sure that a user will click on a specific link to navigate to some page, you can apply this type of prefetching. The method is useful for stable user journey actions, like moving to the shopping cart page after one or several items were added.
Prerendering. This approach means rendering an entire page or some elements of it in advance.
While prefetching is effective, it requires deep user behavior analysis to make precise assumptions.
14. Monitor your speed over time (website speed test)
As you work to improve your site speed, so it’s a good idea to monitor how it changes over time. This is important even after you’ve achieved an acceptable page load time.
As you can see from this post, there are tons of factors that affect your site’s speed so it can change at almost any time.
Monitoring your load times on a regular basis can help you catch any issues early on, and keep your site in good shape.

Conclusion: website speed test and website speed optimization
To better understand the concepts of the website speed test, it is best for our readers to pay more attention to our two previous articles, as these articles provide the necessary metrics to optimize website speed and how you can, make the website speed test.
Websites with low-number page load times perform better on almost all fronts. They rank well in search engines, deliver more positive user experience, and see higher conversions and revenue.
Because average page weight is on the rise, it’s now more important than ever to continuously focus on improving page load time and performance. Open source tools like the coach can help you do this.
It’s also important to remember that while all of the tips on this page can help you achieve your site speed goals, you don’t need to implement all of them today.
Spend some time looking through your site’s speed test results and look for the issues that have the greatest impact on your load times. Focus on those high-impact factors and take the necessary steps to get them into shape.
So, we recommend applying a simple yet effective website speed optimization approach: (website speed test)
- Check and evaluate the key factors of website success, considering conversion, visibility, and usability.
- Test your current website speed and prioritize the pages and features that need the most attention in regard to these three factors.
- Start your optimization with the most speed-reducing aspects and focus on the pages that define your conversion success the most.